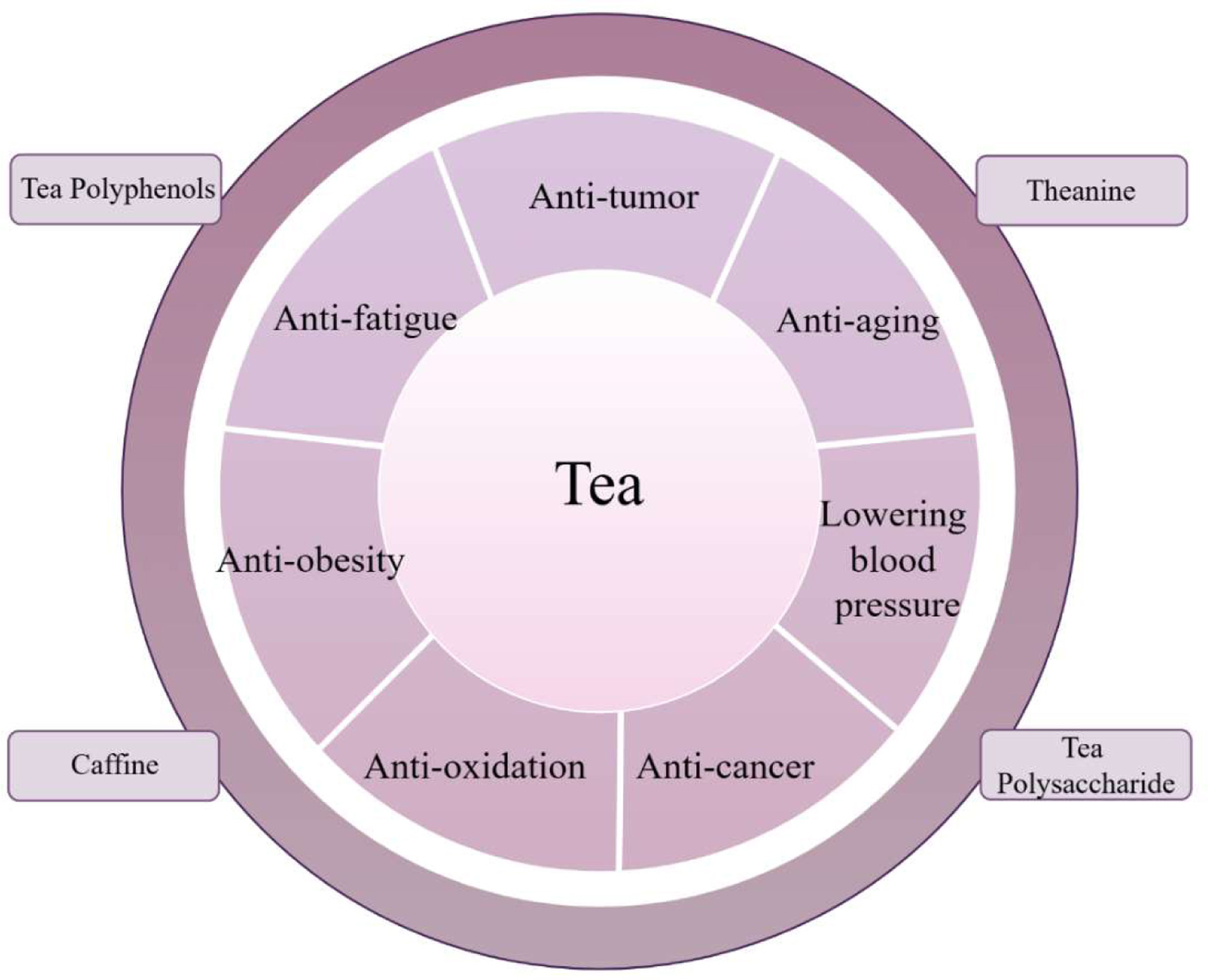
Figure 1. The bioactive components and bioactivities of tea.
| Journal of Food Bioactives, ISSN 2637-8752 print, 2637-8779 online |
| Journal website www.isnff-jfb.com |
Review
Volume 27, September 2024, pages 33-43
Recent advances in the anticancer molecular mechanisms of bioactive components from tea: A review
Figures

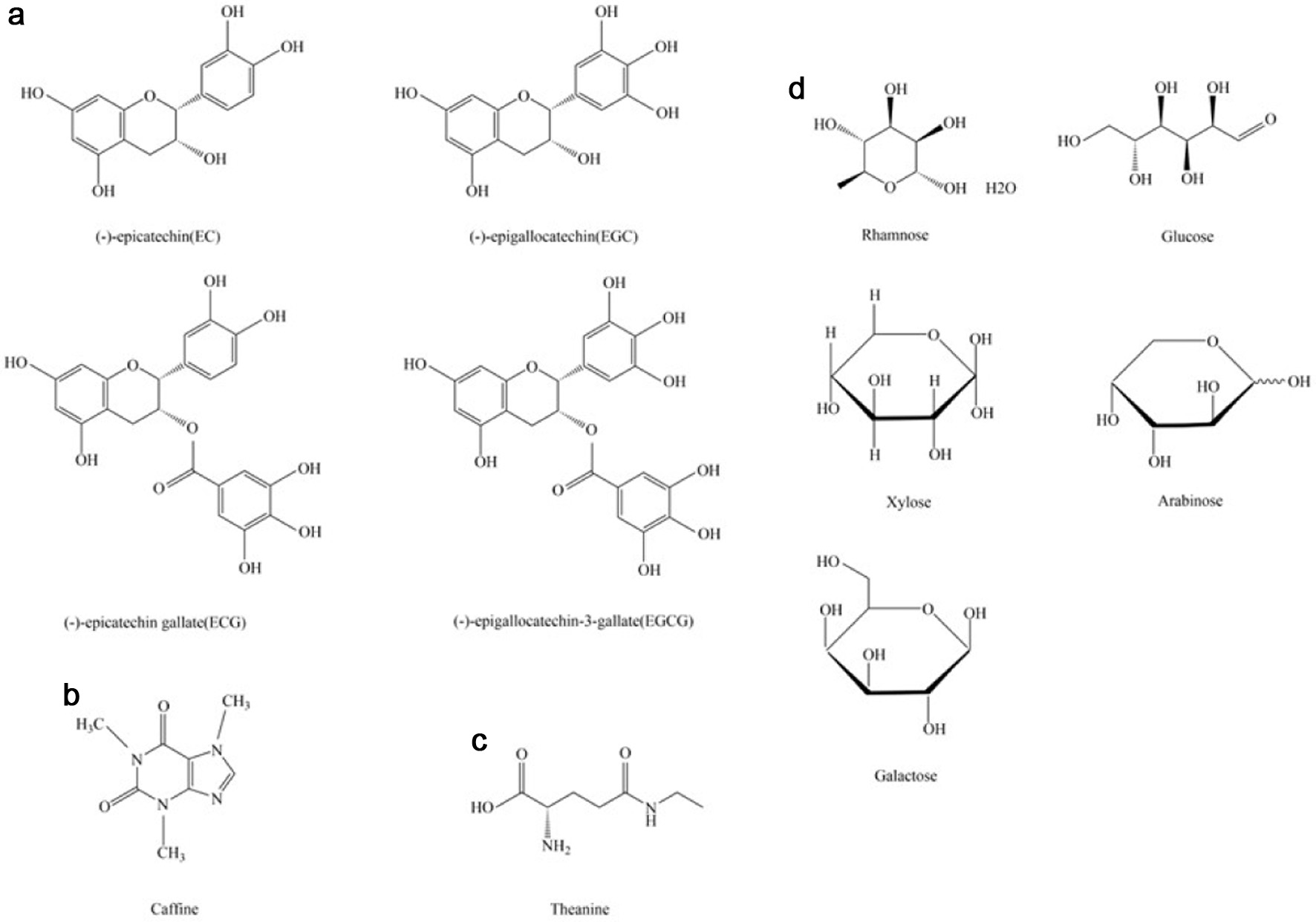
Tables
| Cancer type | Object | Type of tea | Comparison | Metric | Result | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note: aHRs (Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios), RR (Relative Risk), HR (Hazard ratio), OR (Odds ratio), CI (Confidence interval). | ||||||
| Liver cancer (Li et al., 2023) | Chinese females | Tea | Cumulative consume over 30kg vs none | aHRs (95%CI) | 0.56 (95% CI: 0.32–0.97) | 0.038 |
| Liver cancer (Li et al., 2023) | Chinese females | Green tea | Cumulative consume over 30kg vs none | aHRs (95%CI) | 0.54 (95% CI: 0.30–0.98) | 0.051 |
| Bladder cancer (Al-Zalabani et al., 2022) | Overall | Tea | Low vs none | HR (95%CI) | 0.87 (95% CI:0.77–0.98) | 0.004 |
| Bladder cancer (Al-Zalabani et al., 2022) | Overall | Tea | Middle vs none | HR (95%CI) | 0.86 (95% CI:0.77–0.96) | 0.004 |
| Bladder cancer (Al-Zalabani et al., 2022) | Overall | Tea | High vs none | HR (95%CI) | 0.84 (95% CI:0.75–0.95) | 0.004 |
| Ovarian cancer (Zheng et al., 2023) | female | Black tea | Any vs none | RR (95%CI) | 0.64 (95% CI:0.51–0.80) | <0.001 |
| Brain cancer (Song et al., 2019) | Asians | Tea | High vs low | RR (95%CI) | 0.64 (95% CI:0.21–2.02) | 0.026 |
| Brain cancer (Song et al., 2019) | Americans | Tea | High vs low | RR (95%CI) | 0.80 (95% CI:0.76–1.50) | 0.595 |
| Stomach cancer (Martimianaki et al., 2022) | Europeans | Tea | Regular consumption vs non-regular consumption | OR (95%CI) | 1.00 (95% CI:0.90–1.11) | <0.001 |
| Stomach cancer (Martimianaki et al., 2022) | Asians | Tea | Regular consumption vs non-regular consumption | OR (95%CI) | 0.62 (95% CI:0.48–0.81) | <0.001 |
| Stomach cancer (Martimianaki et al., 2022) | Chinese and Japanese | Tea | Regular consumption vs non-regular consumption | OR (95%CI) | 0.67 (95% CI:0.49–0.91) | <0.001 |
| Stomach cancer (Martimianaki et al., 2022) | Iranians | Tea | Regular consumption vs non-regular consumption | OR (95%CI) | 0.50 (95% CI:0.29–0.86) | <0.001 |
| Stomach cancer (Martimianaki et al., 2022) | Americans | Tea | Regular consumption vs non-regular consumption | OR (95%CI) | 0.95 (95% CI:0.87–1.05) | <0.001 |
| Kidney cancer (Chen et al., 2022) | Japanese | Tea | 5cups/days vs rarely | HR (95%CI) | 0.75 (95% CI:0.51–1.12) | 0.39 |
| Kidney cancer (Chen et al., 2022) | Japanese males | Tea | 5cups/days vs rarely | HR (95%CI) | 0.96 (95% CI:0.59–1.56) | 0.74 |
| Kidney cancer (Chen et al., 2022) | Japanese females | Tea | 5cups/days vs rarely | HR (95%CI) | 0.75 (95% CI:0.51–1.12) | 0.05 |
| Prostate cancer (Sen et al., 2019) | Europeans | Tea | High vs low | HR (95%CI) | 0.98 (95% CI:0.90–1.07) | >0.1 |
| Prostate cancer (Sen et al., 2019) | Europeans | Tea | Moderate vs low | HR (95%CI) | 0.98 (95% CI:0.91–1.05) | >0.1 |
| Breast cancer (Zhang et al., 2019) | Chinese females | Green tea | Regular consumption vs none consumption | HR (95%CI) | 0.27 (95% CI:0.09–0.86) | <0.05 |
| Breast cancer (Zhang et al., 2019) | Chinese females | Black tea | Regular consumption vs none consumption | HR (95%CI) | 0.29 (95% CI:0.04–2.08) | <0.05 |
| Breast cancer (Zhang et al., 2019) | Chinese females | Oolong tea | Regular consumption vs none consumption | HR (95%CI) | 1.07 (95% CI:0.49–2.32) | >0.05 |
| Tea type | Composition | Molecular mechanism | Cancer | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green tea | GTPs | circ MITF/miR-30e-3p/HDAC2 axis | Melanoma | Wu et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | L-Theanine | BMAL1 | Melanoma | Zhang et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | Theanine | PGE2/COX-2/MPO/MDA/SOD/GPx/CAT/GR | Colorectal cancer | Ma et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | L-theanine | ERK/NF-κB/P65 | Prostate cancer | Saedmocheshi et al., 2019 |
| Green tea | Tea Polysaccharide | DAB2 | Prostate cancer | Yang et al., 2019 |
| Green tea | Tea Polysaccharide | EB/mTOR/LAMP1 | Colon cancer | Zhou et al., 2021 |
| Black tea | Homogeneous polysaccharide | A549/SMMC7721 | Lung cancer | Liu et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | EGCG | STAT1 | Lung cancer | Li et al., 2023 |
| Golden-flowered tea | PI3K-Akt/MAPK | Lung cancer | Wang et al., 2022 | |
| Green tea | OTP-3 | EGFR | Lung cancer | Huang et al., 2022 |
| Tea | TBs-C | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | Lung cancer | Wang et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | Theabrownin | MAPK/JNK/P53 | Lung cancer | Xiao et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | EGCG | EGFR | Lung cancer | Minnelli et al., 2021 |
| Black tea | NRF2 | Lung cancer | Datta et al., 2023 | |
| Huang qin tea | IL-1β/IL-6/IL-10/TNF-α | Colorectal cancer | Shen et al., 2020 | |
| Green tea | PI3K/AKT | Colorectal cancer | Zhang et al., 2020 | |
| Green tea | EGCG | STAT3/CXCL8 | Colorectal cancer | Zhang et al., 2023; Luo et al., 2020 |
| Green tea | EGCG | GRP5/NF-κB/miR-78 155p/MDR5 | Colorectal cancer | La et al., 2019 |
| Pu-erh tea | Theabrownin | PI3K/AkT/Mtor/cyclin D1 | Colorectal cancer | Leung et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | Theanine | Akt/mTOR/JAK2/STAT3/Smad2 | Colorectal cancer | Shojaei-Zarghani et al., 2021 |
| Cocoa tea | PI3K/Akt | Colorectal cancer | Gao et al., 2020 | |
| Green tea | miRNA-181a | Prostate cancer | Safari et al., 2022 | |
| Black tea | Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate | 67LR/PKCδ/aSMase | Prostate cancer | Sun et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | ECG | acetyl-CoA carboxylase/ATP citrate lyase/fatty acid/PI3K/AKT/mTOR | Prostate cancer | Chen et al., 2021 |
| Green tea | (-)-EC | ZIP9 | Prostate cancer | Thomas and , 2021 |
| Green tea | EGCG | Ca2+ | Prostate cancer | Marchetti et al., 2020 |
| Green tea | EGCG | p53/p21/Bax/Bcl2 | Prostate cancer | Chen et al., 2019 |
| Tea | TLNTs | ROS | Breast cancer | Chen et al., 2023 |
| Gypenia pentaphylua tea | Gyp I | AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin | Breast cancer | Tan et al., 2022 |
| Green tea | p53/p21 | Breast cancer | Santos et al., 2021 | |
| Green tea | EC/EGC/ECG/EGCG | PTP1B | Breast cancer | Kuban-Jankowska et al., 2020 |
| Green tea | EGCG | Arg-1/iNOS/NOX2/NF-κB/STAT3/ECM-receptor interaction/focal adhesion | Breast cancer | Xu et al., 2020 |