Figures
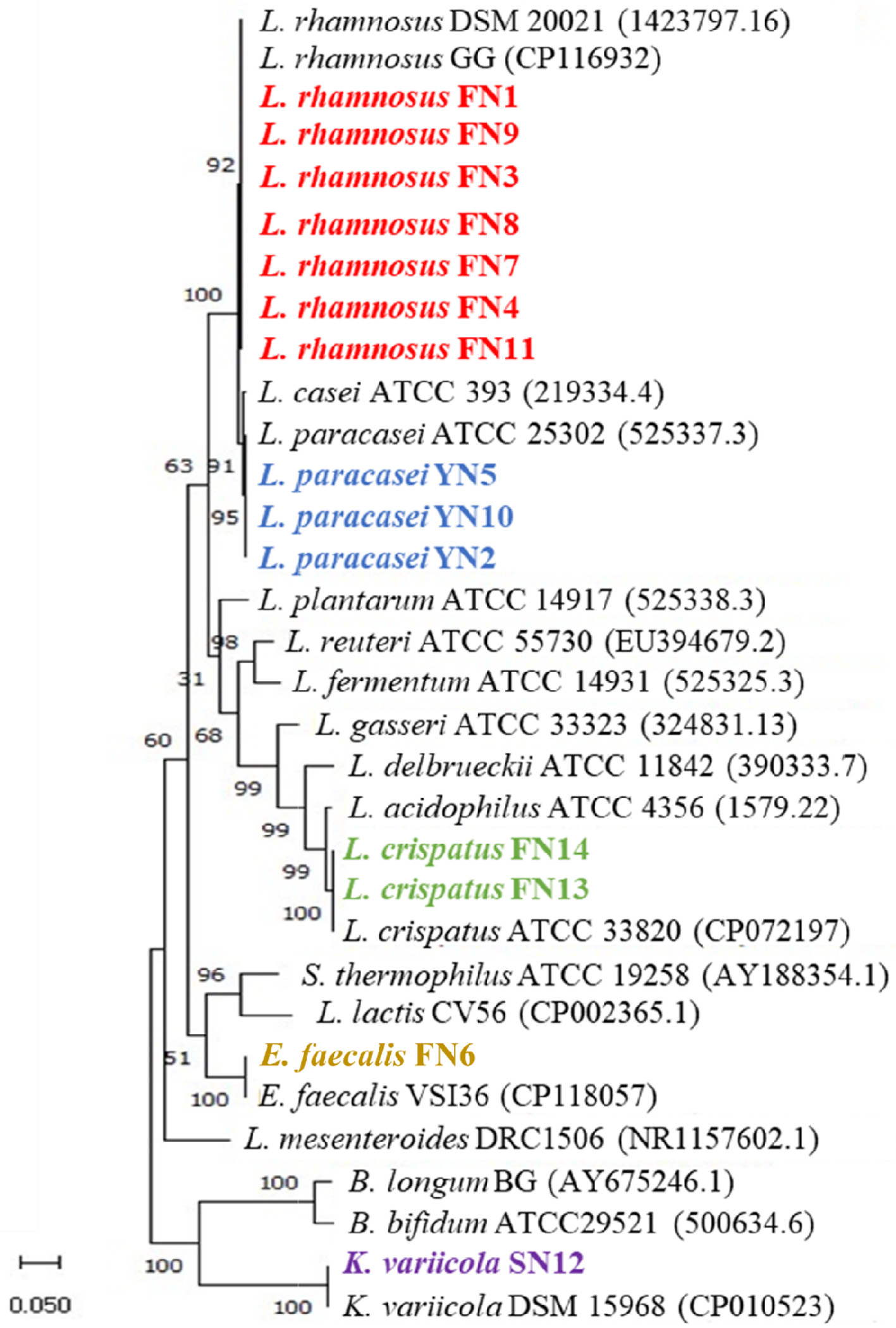
Figure 1. 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic tree of the isolated strains. The tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood method. The bootstrap value expressed as a percentage of 1,000 replicates is given at each node. Nucleotide sequence accession numbers are indicated in parentheses.
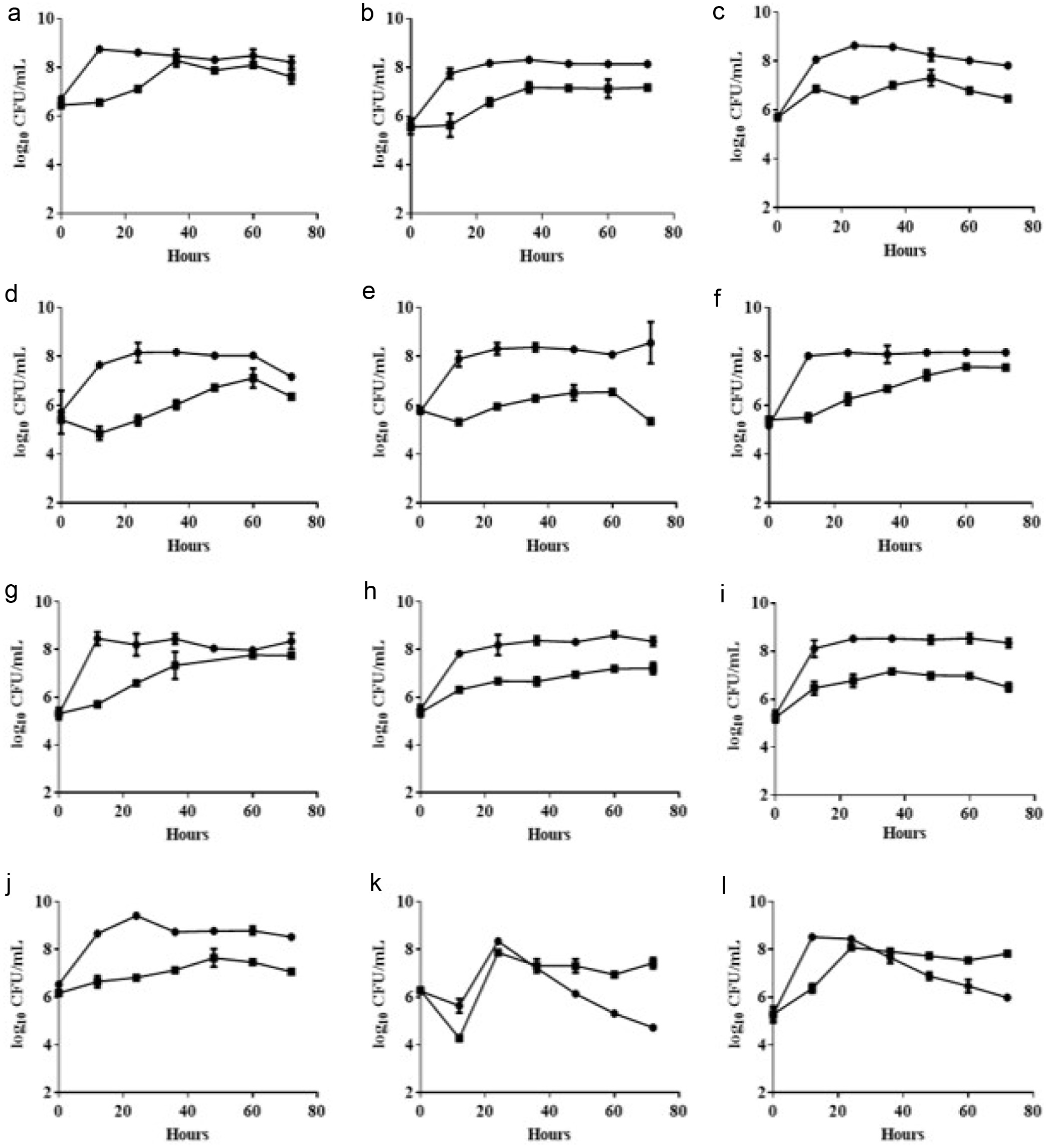
Figure 2. Growth curve of isolated LAB strains in 3% turmeric conditions. MRS medium (circle) and MRS medium containing 3% turmeric (square). (a) L. rhamnosus FN1 (b) L. paracasei YN2 (c) L. rhamnosus FN3 (d) L. rhamnosus FN4 (e) L. paracasei YN5 (f) L. rhamnosus FN7 (g) L. rhamnosus FN8 (h) L. rhamnosus FN9 (i) L. paracasei YN10 (j) L. rhamnosus FN11 (k) L. crispatus FN13 (l) L. crispatus FN14. The 1% of bacterial broth (OD600 = 1.0) was inoculated into the MRS medium containing 3% turmeric powder within the static culture under 37°C for 72 hours. The bacterial growth was evaluated using viable colonies forming unit (CFU). All experiments were carried out in triplicate, and bar values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation.
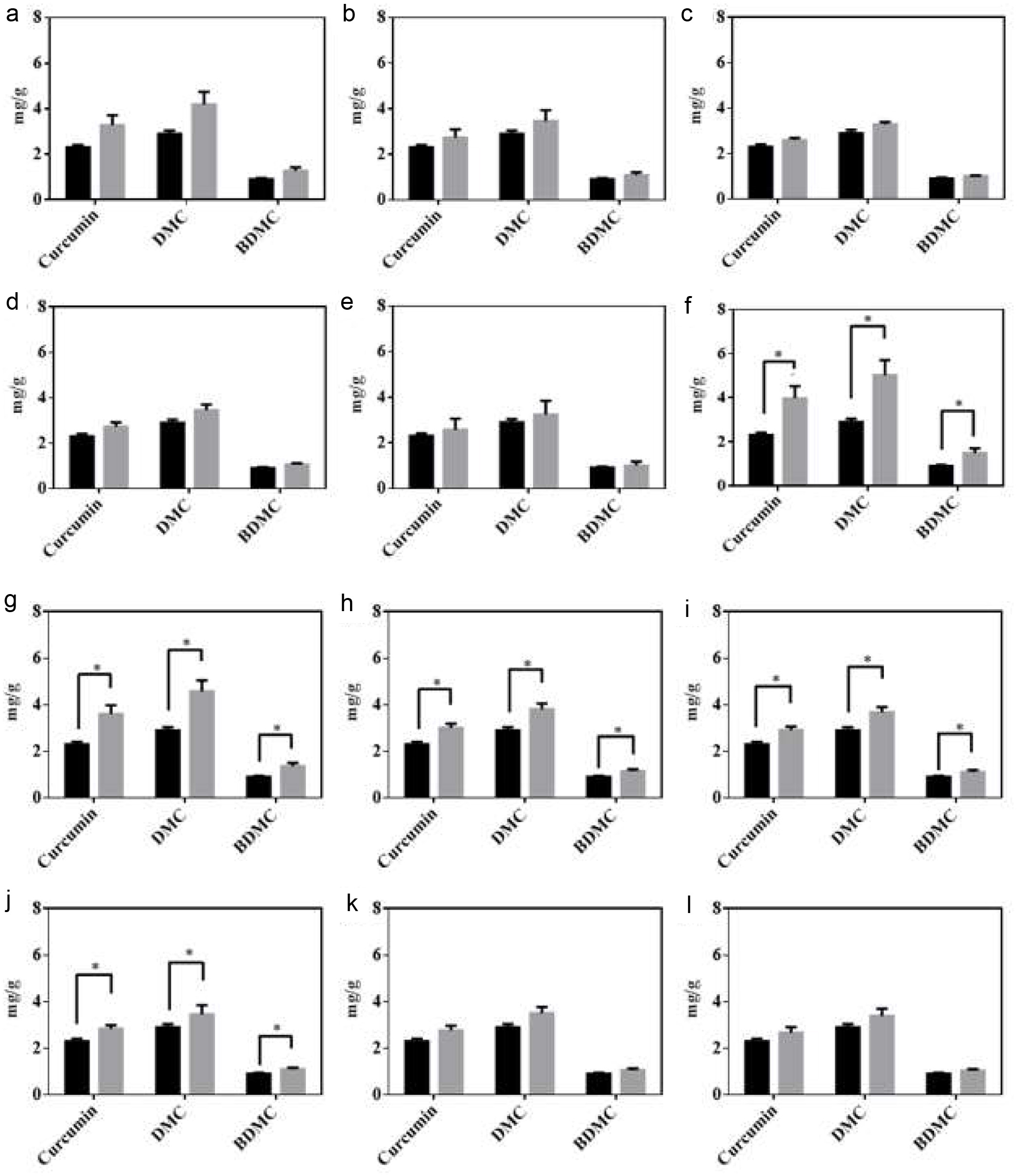
Figure 3. HPLC analysis of curcuminoids in unfermented (black bar) and fermented turmeric (grey bar). (a) L. rhamnosus FN1 (b) L. paracasei YN2 (c) L. rhamnosus FN3 (d) L. rhamnosus FN4 (e) I L. paracasei YN5 (f) L. rhamnosus FN7 (g) L. rhamnosus FN8 (h) L. rhmanosus FN9 (i) L. paracasei YN10 (j) L. rhamnosus FN11 (k) L. crispatus FN13 (l) L. crispatus FN14. After fermentation, curcuminoids were extracted from the freeze-dried fermented turmeric powders and analyzed using the HPLC system comprised of a C18 column with the UV-vis detector (set at 425 nm). All experiments were carried out in triplicate, and bar values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistics were analyzed by unpaired t-test, *p < 0.05.
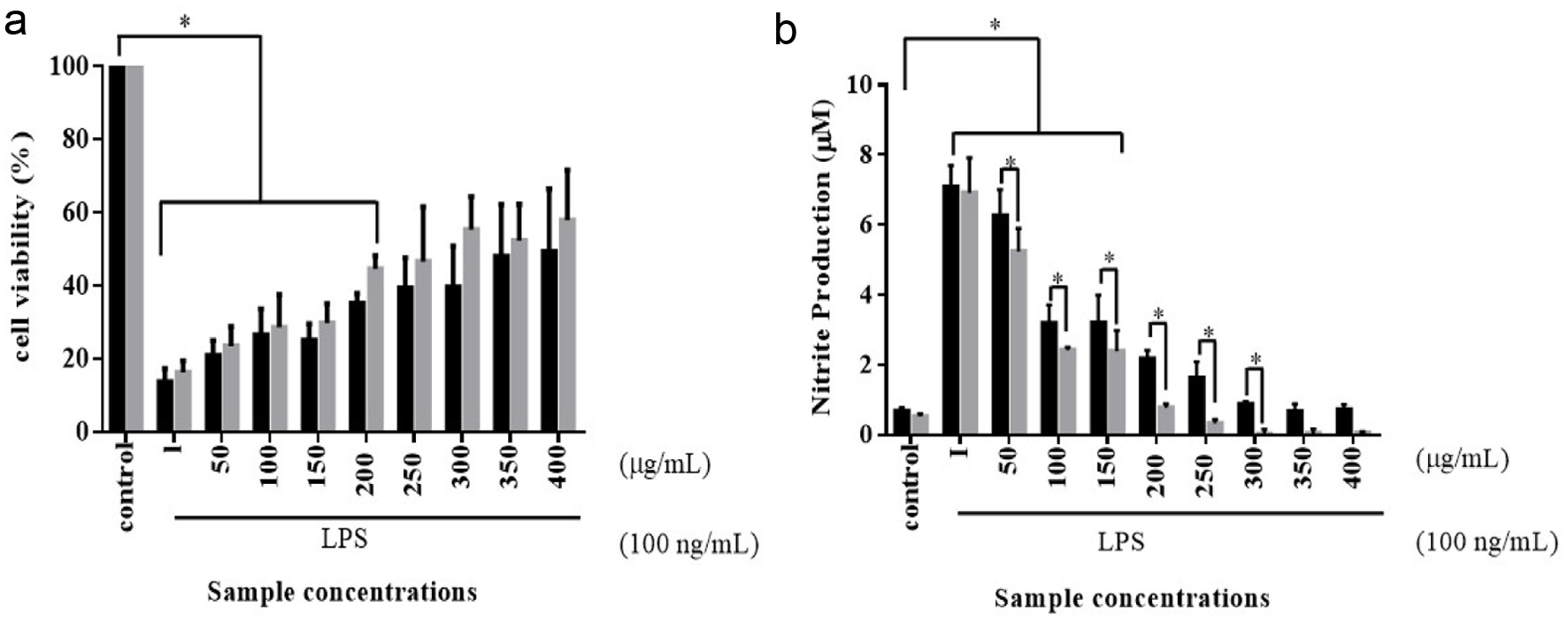
Figure 4. Cell viability (a) and nitrite production (b) of RAW264.7 murine macrophages were treated with various concentrations of unfermented turmeric (black bar) and fermented turmeric (grey bar) for 24 hours. RAW264.7 murine macrophages were cultured with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and treated with various unfermented and fermented turmeric powder for 24 hours under a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C. The cell viability was analyzed using a classical MTT assay, and the Griess assay was used to evaluate the nitrite production. Results were statistically analyzed with the LSD method. Data are present as mean ± SD from at least triplicate wells and three independent experiments. Statistics were analyzed by unpaired t-test, *p < 0.05.
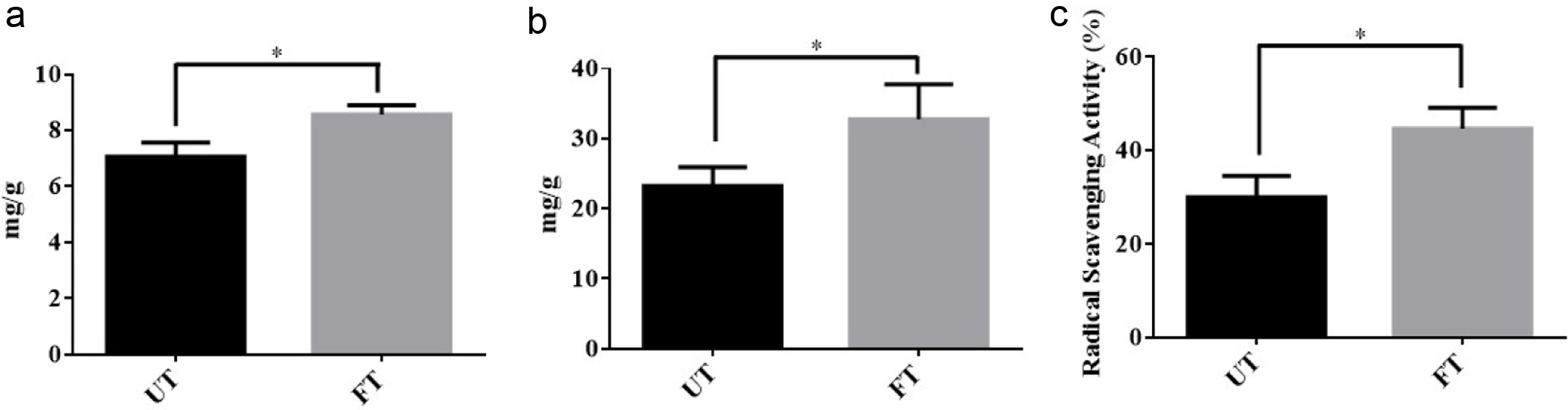
Figure 5. Phytochemical property of fermented turmeric by L. rhamnosus FN7. (a) Total Phenolic Content (b) Total Flavonoid Content (c) Radical Scavenging Activity of unfermented turmeric (UT) and fermented turmeric (FT). Freeze-drying fermented and unfermented turmeric powders were used to extract the total Phenolic and Flavonoid compounds and quantification was performed with a slightly modified Folin-Ciocalteau (FC) method and Aluminium chloride (AlCl3) colorimetric assay, respectively. DPPH analysis was used to evaluate the Radical Scavenging Activity of fermented and unfermented turmeric. All experiments were carried out in triplicate, and bar values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistics were analyzed by unpaired t-test, *p < 0.05.
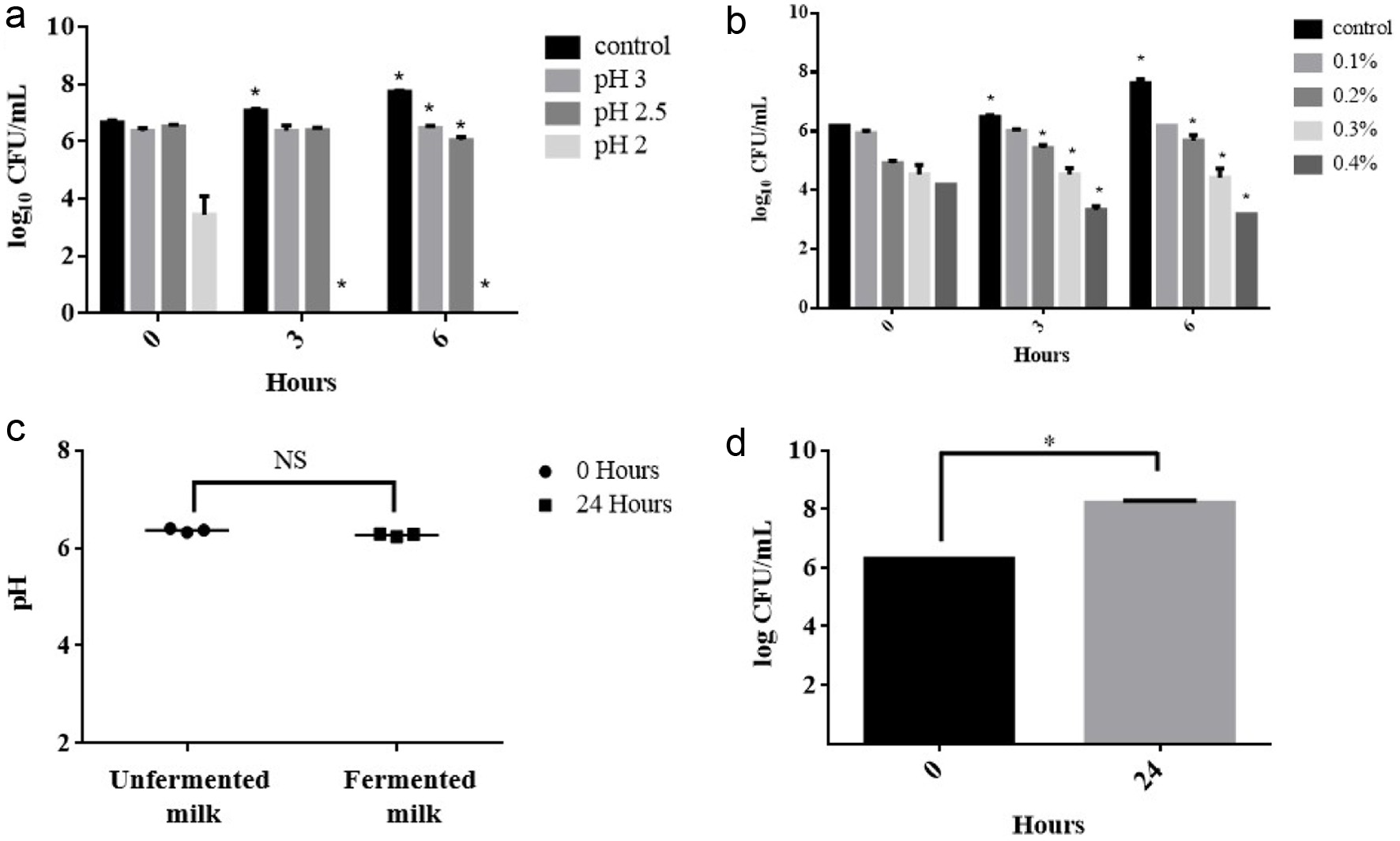
Figure 6. The probiotic property assay of fermented turmeric by L. rhamnosus FN7. (a) pH tolerance, (b) Bile tolerance, (c and d) Milk fermentation capacity. For pH and bile tolerance, the L. rhamnosus FN7 strain was cultured in the MRS medium with different conditions under anaerobic at 37°C for 6 hours. Milk fermentation capacity was performed by incubation of L. rhamnosus FN7 in 10% (w/v) skim milk. The viable colonies forming unit (CFU) was used to evaluate the growth of the L. rhamnosus FN7 strain in all experiments, and the pH of cultured milk was measured. Statistics were analyzed by unpaired t-test, *p < 0.05.





