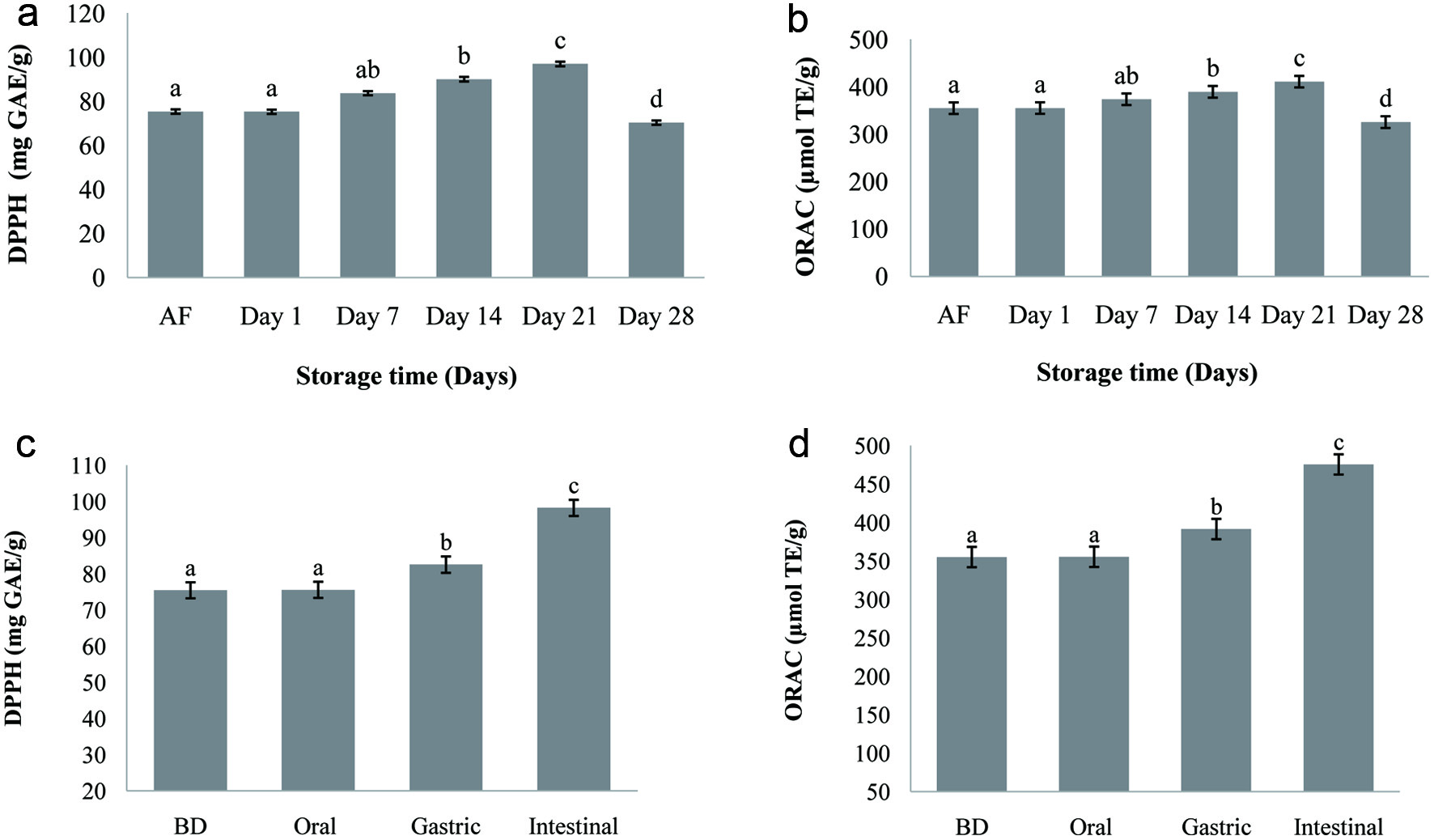
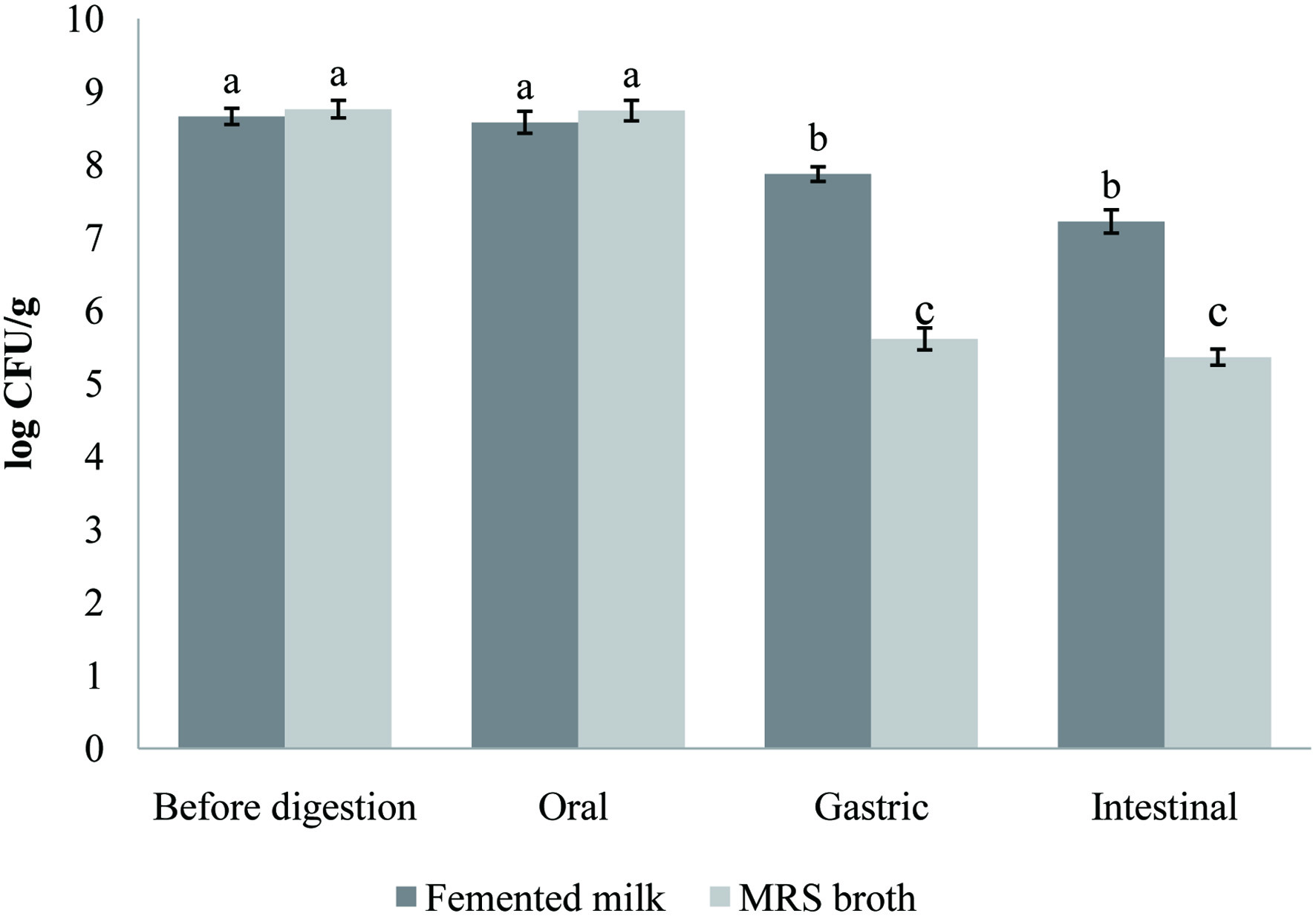
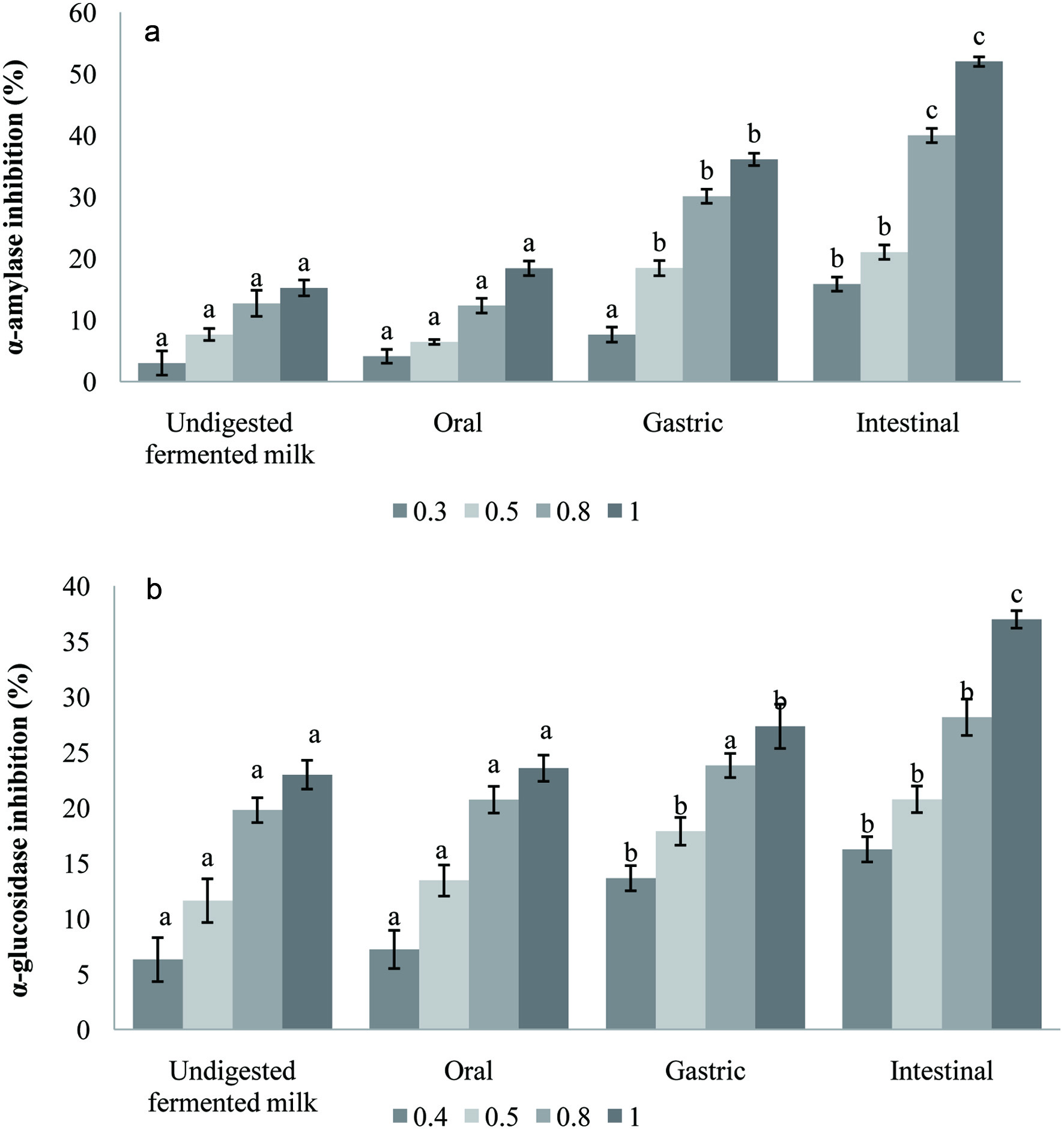
| SM: skim milk, F: fermented milk with only yogurt starter cultures, C: carob powder, I: inulin, FC: fermented milk with carob powder, FI: fermented milk with Inulin, P1: probiotic 1 (Lb. brevis B13), P2: probiotic 2 (Lb. brevis B38), P12: P1 + P2. First column represents the recipe of 4 different treatments for each row; control group (top row), Carob powder added milk (middle row) and inulin added milk (last row). The second column represents what type of prebiotic addition to the formulations; “0” means no addition, “C” means carob powder addition, and “I” means inulin addition. The third column represents the coding for 4 different treatments for each sample group in 3 rows. |